What Is The Cooling Rate Of Granite

Fast and slow cooling of lead iodide.
What is the cooling rate of granite. When magma cools crystals form because the solution is super saturated with respect to some minerals. For this purpose two different cooling procedures are considered the rapid cold water cooling and the slow step by step cooling. This activity is intended for students aged 11 14. If the magma cools quickly the crystals do not have much time to form so they are very small.
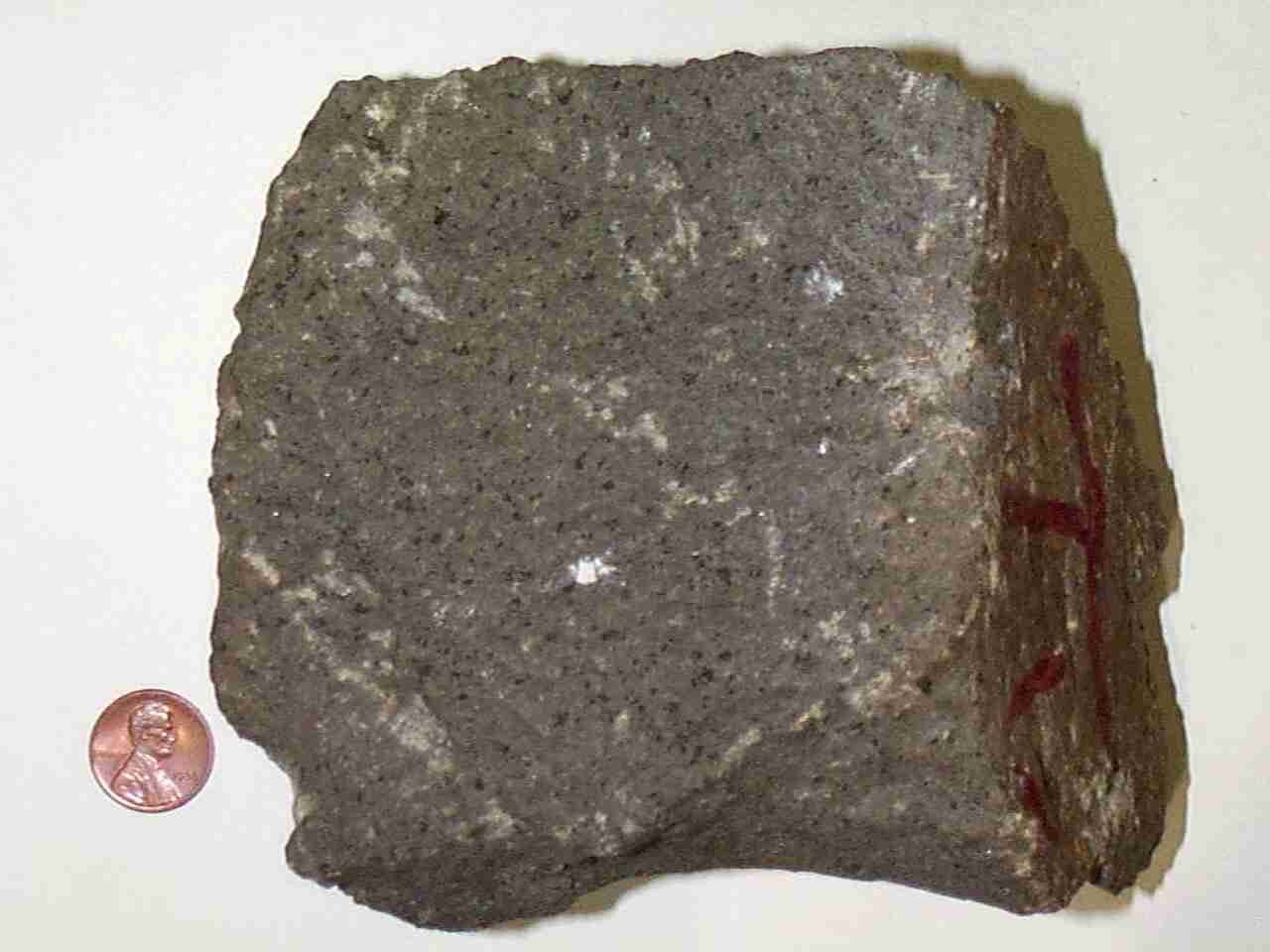
Figure 1 a sample of granite note the large crystals. So you would need to provide some additional information in order to provide a short answer that is correct. Crystal size and cooling rate. Strictly speaking granite is an.
Tuffs commonly contain pumice and rock fragments. As magma cools it begins to crystallise and form solid rock. 6 the claim that coarse grained granite textures need long periods of time to. In general granite is an igneous rock that cools deep below the surface of the earth meaning that it is in contact with rocks that are already hot.
The cooling rate of any object is given by the formula t t ta to ta e kt. Two groups of granite samples are first heated to a desired temperature ranging from 25 c to 900 c and then cooled respectively by using these two methods. Obsidian is an extrusive volcanic rock formed by the rapid cooling of high viscosity magma. The video below is a clip of crystals forming in solution.
Grain size cooling rate. Igneous rocks are made up of several different mineral crystals that grow within the melt as it cools. It is recognized by its glassy texture. Understand how rapid cooling can lead to crystal fractionalization.
Granites can be predominantly white pink or gray in color depending on their mineralogy the word granite comes from the latin granum a grain in reference to the coarse grained structure of such a completely crystalline rock. The rock received its name from german geologist ferdinand von richthofen better known as the red baron a world war i flying ace the word rhyolite comes from the greek word rhýax a stream of lava with the suffix ite given to rocks. Understand the effects of cooling rate on crystal size. Figure 2 a sample of rhyolite the crystals are too small to see.
Crystals in magma grow in a similar way as the melt cools. Recent sceptic arguments citing coarse grained granite texture as a case against rapid cooling of granites are ignoring either wilfully or carelessly previous creationist work which has addressed crystal size and shown it to be an invalid indicator of cooling rate. Granite ˈ ɡ r æ n ɪ t is a common type of felsic intrusive igneous rock that is granular and phaneritic in texture.